Knowledge Base
Frequently Asked Questions
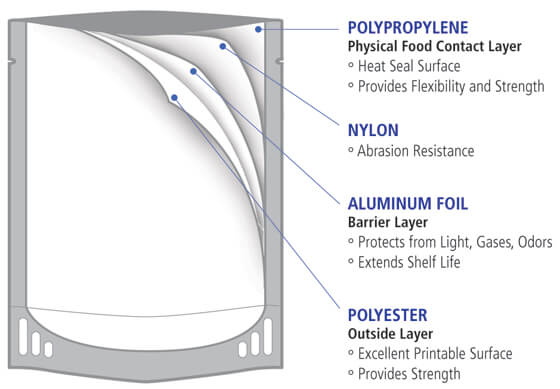
It is a type of packaging which is pliable and has a shape that can be readily changed. Flexible plastic packaging is one of the fastest growing segments in packaging, and is most commonly made from plastic polymers such as polyethylene, polyester, polyamide, and polypropylene.
Its advantages include its low-volume and lightweight structure, as well as the ability to be made from several layers of material to enhance properties like shelf-life, durability, printability, barrier, sealability, and strength. Its flexibility is a key performance factor for many industries.
Flexible packaging is regularly used to wrap products during storage, transport, and to protect products, including food items, during shelf-life.
Most waste-treatment centers do not accept flexible plastic packaging for recycling because its material structure is too complex, contaminated by food, and/or lightweight to be successfully recycled. Of the very few types of flexible packaging that are recyclable, very little (about 4%) are actually recycled. Companies like Teracycle have come to market with mechanical and chemical recycling that address hard to recycle conventional flexible films.
The term ‘biodegradable’ represents a process, but not necessarily under what conditions or time frame, also, the rate of decomposition can vary significantly. Technically, all chemical compounds can be biodegradable under the right conditions, and will decompose over a certain period of time, but that time could be hundreds or thousands of years. For example, wood is biodegradable, but wooden structures don’t break down and can stand for generations. Trees are biodegradable, but stand for hundreds of years. If a material is compostable, it means that under composting conditions (heat, humidity, oxygen, & microorganisms) it will break down to CO2, water, and a nutrient-rich compost within a specific time frame.
Common Abbreviations
- COEX = co extrusion (multiple layers extruded at the same time)
- ADH = adhesive (holds the laminated structures together)
- PE = polyethylene
- LDPE = low density polyethylene
- HDPE = high density polyethylene
- LLDPE = linear low-density polyethylene
- mLLDPE = metallocene linear low-density polyethylene
- PA = polyamide (nylon)
- PET = polyester
- OPP = oriented polypropylene
- BOPP = biaxial oriented polypropylene
- EVOH = ethylene vinyl alcohol
- MET = metalized coating (as in metalized polyester)
- AOH = acrylic alcohol coating
- PVOH = polyvinyl alcohol coating
- PVDC = polyvinylidene chloride coating
- SiOx = silicon oxide coating
- AlOx = aluminum oxide coating